Are all orthodontists Board Certified?
Not all orthodontists are board certified. While all orthodontists must be licensed to practice, currently, only about one-third pursue board certification. The American Board of Orthodontics (ABO) certification process is a significant achievement, representing a step beyond the two to three years of advanced education required to become a specialist in orthodontics. This process involves:
- Demonstrating accomplishments in patient care through detailed case reports that cover a broad range of patient problems.
- Undergoing a thorough interview by a highly respected panel of examiners to assess orthodontic knowledge, clinical skills, and judgment.
Board certification is a voluntary process that not all orthodontists choose to pursue.
How many certifying boards are recognized by the American Dental Association in the specialty of orthodontics?
There is only one: The American Board of Orthodontics (ABO). Established in 1929, the ABO is the oldest specialty board in dentistry and is recognized by the American Dental Association. Its purpose is to elevate the quality of orthodontic care by promoting excellence through certification, education, and professional collaboration.
Why would an orthodontist choose to complete this voluntary certification process?
Completing the ABO certification process signifies an orthodontist’s highest commitment to excellence in the field. This achievement:
- Demonstrates the necessary knowledge base and skills to treat patients to the highest standards.
- Reflects a commitment to staying updated with the latest advances in patient care and continuously delivering these innovations to patients.
- It is considered by many orthodontists as a symbol of commitment to the specialty and a significant personal accomplishment.
What steps are required to complete the ABO certification process?
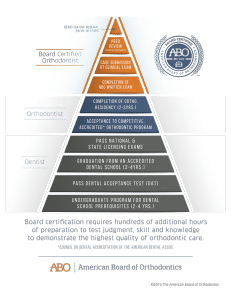
The certification process involves several rigorous steps:
- Written Examination: A comprehensive 240-question exam covering various areas of orthodontic knowledge.
- Clinical Examination: Presentation of detailed case reports from their practice or residency, showcasing a history of excellence in patient care. These cases are evaluated by a panel of examiners and later discussed during an oral examination, testing the applicant on a wide range of academic and clinical topics.
- Certification Renewal: Every 10 years, certified orthodontists must renew their certification, demonstrating continued excellence in patient care to maintain their certification status.
For further information about The American Board of Orthodontics and Board Certification, click here.
